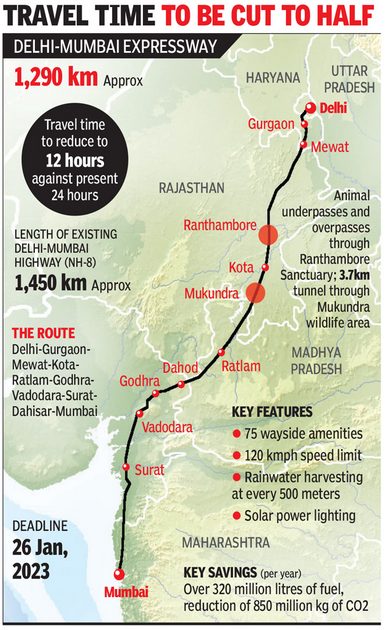
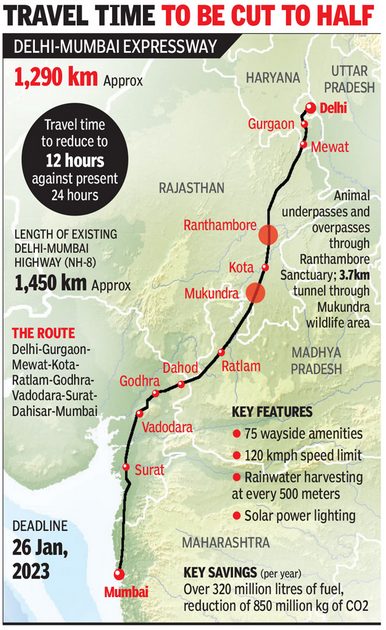
Delhi-Mumbai Expressway A monumental infrastructure project undertaken by the National Highways Authority of India (NHAI), stands as a testament to India’s commitment to enhancing its transportation network. Stretching over 1,350 kilometers, this eight-lane (expandable to 12-lane) expressway is poised to connect the nation’s capital, New Delhi, with its financial hub, Mumbai.
Delhi Mumbai Expressway Key Facts
- Project Inception:
- The foundation stone for the Delhi-Mumbai Expressway was laid on March 8, 2019, by Union Minister Nitin Gadkari, in the presence of Sushma Swaraj and Arun Jaitley.
- The project is currently partially operational, and its total cost, including land acquisition, amounts to around ₹1,00,000 crores (~US$13.1 billion).
- Strategic Route:
- The expressway is strategically designed to connect the Sohna Elevated Corridor in Delhi to the Jawaharlal Nehru Port in Maharashtra.
- It traverses through Delhi, Haryana, Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh, Gujarat, and Maharashtra, playing a crucial role in the Delhi-Mumbai Industrial Corridor.
- Length and Spur Routes:
- The main stretch of the expressway spans 1,198 kilometers, with two additional spurs – the DND–Faridabad–KMP (59 km) and Virar–JNPT (92 km) – extending its total length to 1,350 km.
- Construction and Expansion:
- Initially, the expressway is eight lanes wide, and the greenfield alignment incorporates a route through less developed areas, reducing the travel time from 24 to 12 hours.
- Provisions are made for reserving land in the middle of the road for future expansion, ensuring the flexibility to accommodate growing traffic demands.
National Highways Authority of India (NHAI):
The NHAI, the implementing agency behind the Delhi-Mumbai Expressway, plays a pivotal role in developing and maintaining the country’s highway infrastructure. Here are some key facts about NHAI:
- Establishment and Mandate:
- Established in 1988, NHAI operates under the Ministry of Road Transport and Highways, Government of India.
- Role in Infrastructure Development:
- NHAI has been instrumental in spearheading various ambitious projects aimed at enhancing road connectivity across the nation, including the development of expressways and economic corridors.
- Technological Integration:
- The authority has embraced technological advancements for efficient project management, toll collection, and real-time monitoring of road conditions.
- Public-Private Partnerships (PPPs):
- NHAI often engages in PPPs to fund and execute large-scale infrastructure projects, ensuring a collaborative approach for sustainable development.
Construction Phases:
To efficiently execute the colossal Delhi–Mumbai Expressway project, the entire 1,350 km stretch has been meticulously divided into four distinct sections, comprising a total of 52 construction packages or tenders. The length of each package varies, ranging from 8 km to 46 km.
Section-wise Breakdown:
- DND–Faridabad–KMP:
- Length: 59 km
- Number of Packages: 3
- State-wise Distribution: 1 in Delhi and 2 in Haryana
- Sohna–KMP–Vadodara:
- Length: 844 km
- Number of Packages: 31
- State-wise Distribution: 3 in Haryana, 13 in Rajasthan, 9 in Madhya Pradesh, and 6 in Gujarat
- Vadodara–Virar:
- Length: 354 km
- Number of Packages: 13
- State-wise Distribution: 10 in Gujarat and 3 in Maharashtra
- Virar–JNPT:
- Length: 92 km
- Number of Packages: 5
- State-wise Distribution: All 5 in Maharashtra
Comprehensive Overview:
- Total Length: 1,350 km
- Total Number of Packages: 52
- Spanning Across 6 States
Project Finance Facts
- The project divides into 52 packages, with 31 operating under the Engineering, Procurement, and Construction (EPC) model for the Sohna–Vadodara segment.
- The remaining 21 packages operate under the Hybrid Annuity Model (HAM).
- The HAM Model combines elements of the EPC Model and Build-Operate-Transfer (BOT) Model.
- Under HAM, the Government of India contributes 40% of the project cost in trenches linked to milestones.
- Contractors are responsible for arranging the remaining 60% of the project cost.
World Record for Construction:
- In Gujarat, contractor Patel Infrastructure achieved a world record by laying Pavement Quality Concrete (PQC) over a stretch of 2.58 km in a 4-lane width (4×2.58 = 10.32 lane km) within 24 hours.
- The PQC laying commenced on February 1, 2021, at 8 am and concluded the next day at 8 am.
- A German-made Wirtgen concrete paving machine, with a width of 18.75 meters, was utilized for this remarkable feat.
Unique Features Delhi Mumbai Expressway :
- Wayside Amenities:
- 93 locations on the expressway will host Wayside Amenities, including ATMs, hotels, retail shops, food courts, charging stations for electric vehicles, fuel stations, helipads, and fully equipped trauma centers every 100 km.
- It becomes the first expressway to host numerous amenities and necessary facilities around its stretch.
- Electric Highway:
- A stretch of the expressway is designated as an e-Highway, allowing trucks and buses to run at 120 km/hour, reducing logistics costs by 70% with the use of electricity.
- The project includes 4 dedicated lanes for electric vehicles.
- Environment-Friendly Design:
- Developed as an eco-friendly expressway with a tree cover of 20 lakh trees, drip irrigation along the entire stretch, and rainwater harvesting every 500 meters.
- Illuminated using a mix of state grid power supply and solar energy.
- Wildlife Crossings:
- 2.5 km of the expressway features 5 wildlife crossings in identified wildlife corridors, including a first-of-its-kind 8-lane wide tunnel in Mukundara Hills National Park.
- Measures like noise barrier walls and protective barriers aim to minimize the impact on wildlife.
- Inter-connectivity:
- It provides inter-connectivity options and direct access to other expressways such as Delhi–Noida Direct Flyway, Western Peripheral Expressway, amd Trans-Haryana Expressway.
- Connect to major expressways in Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra, and Telangana.
- Side Spurs:
- Future plans include additional side spurs for enhanced connectivity to major cities and other areas.
- Notable additions include the Faridabad-Jewar-Khurja Expressway and the operational Bandikui-Jaipur Expressway spur.
Delhi-Mumbai Expressway, a flagship project of NHAI, is not merely a stretch of concrete but a transformative conduit that connects regions, fosters economic growth, and symbolizes India’s commitment to modernizing its transportation infrastructure. As NHAI continues to lead the charge in developing and maintaining the national highway network, the Delhi-Mumbai Expressway stands as a shining example of India’s progress in the realm of infrastructure development.
The Highway Man of rising India

- Nitin Gadkari was born on May 27, 1957, in Nagpur, Maharashtra, India.
- He holds a Bachelor’s degree in Commerce and a degree in law from the University of Nagpur.
- He served as the youngest president of the Bharatiya Janata Yuva Morcha at the age of 24.
- In 2009, he took charge as the President of the Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP).
- As the Union Minister for Road Transport and Highways, he has initiated key projects to boost connectivity.