Indian Air Force

The roots of the Indian Air Force (IAF) trace back to its inception as the Royal Indian Air Force on October 8, 1932, during British colonial rule. The primary objective of this fledgling force was to provide air support to the British Army in India.
World War II
During World War II, the Royal Indian Air Force played a crucial role in various theaters of conflict. Squadrons were deployed in North Africa, the Middle East, and Southeast Asia, showcasing the competence and potential of Indian aviators.
Post-Independence Transition
As India gained independence in 1947, the Royal Indian Air Force transitioned into the Indian Air Force. The prefix “Royal” was dropped, symbolizing the detachment from the British monarchy.
First Indo-Pak War – 1947-48
The IAF saw its first combat during the First Indo-Pak War of 1947-48. The conflict over Kashmir witnessed the IAF conducting strategic airlifts and providing air support to ground forces.

Early Modernization: In the following decades, the IAF focused on modernization, gradually phasing out older aircraft and incorporating newer, more advanced models. The induction of jet aircraft marked a significant leap in technological capabilities.
1965 Indo-Pak War: The 1965 Indo-Pak War presented a testing ground for the IAF. While the conflict ended in a stalemate, the IAF showcased its strategic and tactical acumen, highlighting the need for continuous modernization and readiness.
Bangladesh Liberation War – 1971
The 1971 Indo-Pak War, also known as the Bangladesh Liberation War, stands as a defining chapter in the history of the IAF. Swift and coordinated air operations played a crucial role in securing victory for India and the creation of Bangladesh.

Kargil War – 1999:

The Kargil War in 1999 marked another significant chapter in the IAF’s history. The force played a crucial role in evicting infiltrators from strategic heights in the Kargil sector, demonstrating precision airstrikes and air superiority.
Modern Era and Technological Advancements: In the 21st century, the IAF has undergone extensive modernization efforts. The induction of advanced fighter jets, reconnaissance aircraft, and strategic assets has enhanced its operational capabilities.
Humanitarian Assistance and Disaster Relief: The IAF’s role extends beyond military operations. It actively engages in humanitarian assistance and disaster relief operations, showcasing its versatility and commitment to national and regional security.
Indigenous Developments: Emphasizing self-reliance, the IAF has been involved in the development of indigenous aircraft like the Light Combat Aircraft (LCA) Tejas. This reflects a commitment to reducing dependence on foreign acquisitions.
Present and Future: As of my last knowledge update in January 2022, the IAF continues to adapt to emerging challenges. Future plans include further modernization, incorporating cutting-edge technologies, and maintaining a high level of readiness to safeguard the nation’s interests.

The Indian Air Force, with a rich history spanning nearly nine decades, stands as a symbol of valor, professionalism, and technological prowess, dedicated to securing the skies and contributing to India’s defense and progress.
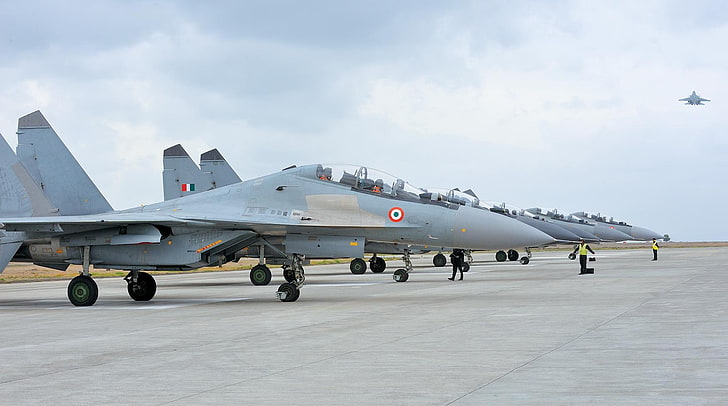

- Establishment:
- The Indian Air Force (IAF) was officially established on October 8, 1932, as the Royal Indian Air Force during British colonial rule.
- Post-independence in 1947, it transitioned into the Indian Air Force, with the prefix “Royal” being dropped.
- Motto:
- The motto of the Indian Air Force is “Nabha Sparsham Deeptam,” which translates to “Touch the Sky with Glory” in Sanskrit.
- Leadership:
- The Chief of the Air Staff, a four-star air officer, is the highest-ranking officer in the Indian Air Force.
- Air Chief Marshal Rakesh Kumar Singh Bhadauria served as the Chief of the Air Staff as of my last knowledge update in January 2022.
- Operational Commands:
- The Indian Air Force is divided into operational commands, each responsible for a specific geographical area. These include Western Air Command, Eastern Air Command, Central Air Command, Southern Air Command, and South Western Air Command.
- Strategic Forces:
- The IAF plays a crucial role in India’s nuclear deterrence strategy. It operates strategic bombers and is capable of delivering nuclear weapons as part of the country’s defense capabilities.
- Aircraft Fleet:
- The IAF maintains a diverse fleet of aircraft, including fighter jets, transport planes, helicopters, and reconnaissance aircraft.
- Notable fighter aircraft in the IAF’s inventory include Sukhoi Su-30MKI, Dassault Rafale, and the indigenous Light Combat Aircraft (LCA) Tejas.
- Strategic Assets:
- The IAF operates strategic and surveillance assets such as airborne early warning and control (AEW&C) systems, ensuring advanced situational awareness and command capabilities.
- Humanitarian Operations:
- The Indian Air Force actively engages in humanitarian assistance and disaster relief operations both within India and in neighboring countries.
- Operations like “Op Rahat” showcased the IAF’s ability to respond swiftly to natural disasters, evacuating civilians and delivering aid.
- Indigenous Development:
- The IAF is committed to indigenization and self-reliance in defense production. The development of the indigenous Light Combat Aircraft (LCA) Tejas and ongoing projects like the Advanced Medium Combat Aircraft (AMCA) demonstrate this commitment.
- Awards and Honors:
- The Indian Air Force has been honored with numerous awards, including individual gallantry awards like the Param Vir Chakra and Maha Vir Chakra, which recognize acts of exceptional courage and bravery.
- Global Collaboration:
- The IAF actively participates in joint military exercises with air forces of various nations, fostering collaboration, and promoting interoperability.
- Technology Integration:
- The Indian Air Force integrates advanced technologies, including Artificial Intelligence (AI) and unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), to enhance its operational capabilities and maintain a technological edge.
- Academic Institutions:
- The IAF has established educational institutions such as the Air Force Academy in Hyderabad, where officers, pilots, and technical personnel undergo rigorous training.
- Kargil War:
- The IAF played a crucial role during the Kargil War in 1999, executing precision airstrikes and securing air superiority in the conflict zone.
- Future Modernization:
- The IAF continues to focus on modernization and upgrading its capabilities, with plans for acquiring advanced aircraft, systems, and technologies for future challenges.
Famous Aircrafts in Indian Air Force Fleet